CO₂-LASER PROCESSING
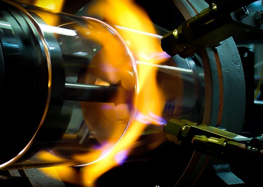
CO2-Lasers offer great potential in the processing of glass, ceramics, sapphire and metals. The technology allows the use of various methods for joining and cutting as well as of procedures for surface treatment.
Especially for industrial applications of CO2-Lasers, the research conducted at ifw Jena brings new processing methods and ways to optiize existing processes.
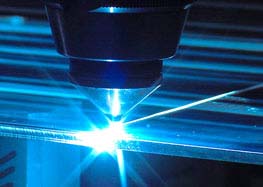
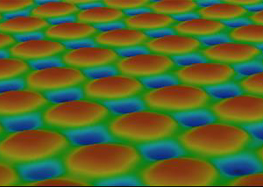
The main focus of our research lies on the interaction of the CO2 laser beam with a 10,6 µm wavelength and different materials during surface absorption of different materials. To this end, we investigate different beam forming and beam guidance techniques. The aim of our research is to minimize stress during melting and joining processes in order to enhance their efficiency.

Dipl.-Ing. (FH) Thomas Schmidt +49 3641 204-198 E-Mail schreiben

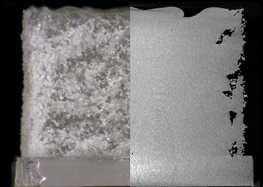
A further aspect of our work involves the development of new process strategies for short-pulse CO2-laser cutting and ablation with the help of a specially modified nanosecond CO2-laser. Its short and therefore extremely intense pulses alter the material in a manner which makes athermal ablation possible. As a result, temperature-sensitive materials with high coefficients of expansion can also be processed.
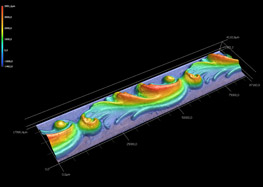
To expand our knowledge base extensive tools for feedback control as well as measurement benchmarking are available. These tools ensure a better understanding of laser-material interactions and also increase the reliability and reproducibility of application-related process investigations.
Recent Projects in the field of CO₂-Laser processing


Ceramic H₂ sensor development of a ceramic pressure sensor platform for hydrogen management of the industrial materials management of the future.
more

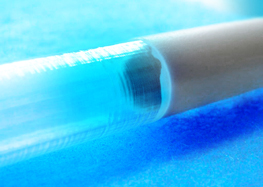
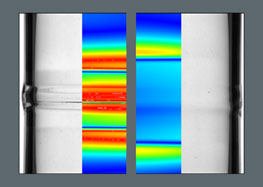
Development of a method for warm-soft calibration of the outside diameter of glass tubes with high precision
more


Entwicklung eines Verfahrens zur Kalibrierung von Hohlglas mittels Laserstrahlung und angepasster Strahlformung
more