MultiDiff

Förderkennzeichen: 49MF220053
Projektlaufzeit: 01.09.2022 bis 31.08.2024
Multiple diffusion bonding per furnace cycle
Aim of the development
The project aimed to develop new production technology approaches that differ significantly from classic diffusion bonding. In order to join several components in a single furnace cycle, the component geometry must be the same and the height tolerances must match within narrow limits. By using compensating foils or by developing a pressure chamber, the welding processes can be produced independently of the geometry. In this case, the pressure transfer on all sides and homogeneous surface pressure on the components is carried out by a medium. Height tolerances could thus be largely neglected. On the basis of a simulation model and in the context of joining technology investigations, a production strategy was developed in the project and the feasibility of multiple welding processes per furnace cycle was demonstrated. A qualitative characterization of the welded composites of the aluminium alloys AW6082 and AW6060 was carried out on the basis of material testing methods. Advantages and disadvantages of the process concepts were analyzed and evaluated and iteratively included in the process development, which stood for the economic efficiency, production rates and unit cost reduction of the process concept to be developed.
Advantages and solutions
Together with industrial companies, basic details on component design, a requirements profile, target parameters, required surface quality and component quality were initially defined in a process strategy.
The approach pursued in the project consists of the further development of diffusion bonding in terms of production technology, scaling from single to multiple production per furnace cycle, through ...
... targeted compensation of manufacturing tolerances on semi-finished components through the use of graphite foils for multiple welds.
... pressure chamber with a filling medium. In this case, isostatic pressure is transferred to the components by a fixed compensation body, which means that height tolerances can be largely neglected.
Diffusion bonding is a pressure welding process in which the connection is made in a solid state without a molten phase. In order to be able to produce high-quality diffusion-welded components, a process-reliable, homogeneous application of force across all components must be ensured. The process concepts developed provide the prerequisites for compensating height tolerances compared to classic diffusion bonding with pressure plates.
The following development steps were carried out:
- Definition of the statistical test plan, the specimen geometry, as well as the characterization and evaluation of the welding materials.
- Definition of the compensation body design (graphite foils) and their characterization and evaluation as well as individual diffusion welding experiments with simultaneous welding parameter optimization.
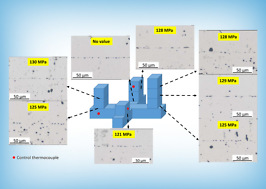
- Characterization and evaluation of the bond quality of the joining zone, the overall deformation of the components, as well as the behavior of the compensation bodies after the individual diffusion welding experiments.
- Determination of characteristic values for FEM simulations and model extension to multiple welding applications as well as FEM modeling of the influence of compensation bodies and pressure chamber on the welding result as a function of the welding parameters.
- Production of a pressure chamber and diffusion welding experiments of multiple welds as well as a material characterization of the joints and the deformation behaviour.
At the same time, the thermal behavior of the filling medium and the pressure chamber as well as welding parameter adjustments were considered. Recommendations for action were derived from the test results. The results obtained can be directly incorporated into the design of a wide range of component geometries and materials in order to qualify them for technical applications. In addition, recommendations and guidelines for the implementation of diffusion bonding tasks were made available to users in a timely manner and an assessment of productivity, additional effort and cost comparison was carried out.
Target market
Due to the constantly increasing requirements and demand for components and component systems with internal free-form structures as well as high-strength and large-area joints, diffusion bonding is increasingly becoming the focus of industrial applications. There are already several small and medium-sized companies that offer diffusion bonding as a commercial service. This joining technology is used to produce near-contour tempering channels in injection molds for plastic molding or in toolmaking.
Other applications are in areas where thermal processes are the key components, for example as heat exchangers, heat conducting foil assemblies in optoelectronic devices for the aerospace industry. The potential for the production of complex-shaped components made of titanium, copper or aluminum alloys or heat-resistant steels was demonstrated in the project and is still considered to be high. The technology complements existing production processes and offers the opportunity to open up new products and fields of technology, for example in additive manufacturing. Ceramic and silicate materials are also becoming increasingly important in the energy transition and in resource-efficient manufacturing.
The transfer of R&D results takes place directly with potential users. Based on our expertise, the transfer takes place through feasibility studies, prototype production through to small series production. Furthermore, this also takes place via consulting services through to the transfer of technology to companies and thus also makes a contribution to technical services or contract research.