USP Diffusor

Förderkennzeichen: 49MF210153
Projektlaufzeit: 01.12.2021 bis 30.11.2023
Manufacturing of individual diffusors by means of USP-lasers
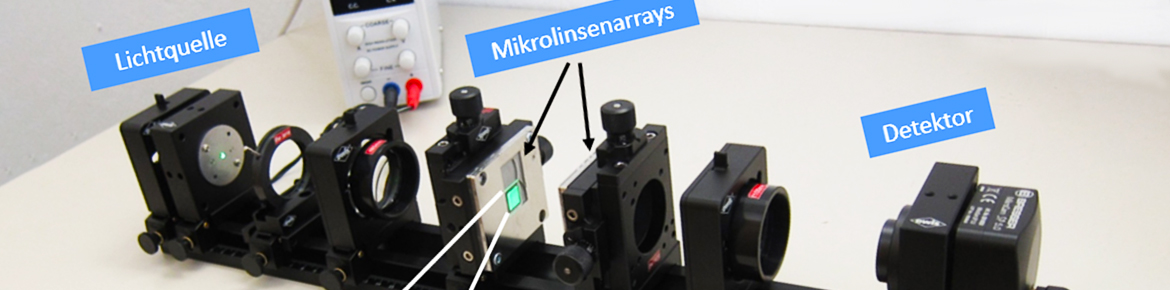
In sensor technology, diffusers are used to scatter incident radiation onto the sensor: Optical sensors are often located in a housing with a window, which limits their detection angle; diffusers can expand the detection angle. Especially with UV sensors, manufacturers face the challenge that the diffuser must withstand all environmental conditions for which the sensor was also built. However, many glass materials absorb UV radiation and degrade when exposed to it.
The goal of the project is to use laser radiation to create scattering centers in fused silica so that the fused silica can be used simultaneously as a diffuser and a window for UV sensors. These diffusers should be stable over a long period of time under UV irradiation and not show any significant absorption. For this purpose, two scattering mechanisms are to be investigated: First, microdots are to be arranged in the quartz that have a different refractive index than the surrounding glass in order to create a scattering structure. Secondly, small cavities, voids, are to be created in the quartz glass, which act as diffusers like air bubbles.
The goal of the project is to use laser radiation to create scattering centers in fused silica so that the fused silica can be used simultaneously as a diffuser and a window for UV sensors. These diffusers should be stable over a long period of time under UV irradiation and not show any significant absorption. For this purpose, two scattering mechanisms are to be investigated: First, microdots are to be arranged in the quartz that have a different refractive index than the surrounding glass in order to create a scattering structure. Secondly, small cavities, voids, are to be created in the quartz glass, which act as diffusers like air bubbles.