PUNKT

Förderkennzeichen: 01IF00048L
Projektlaufzeit: 01.11.2021 bis 29.02.2024
Welding of multi dimensional structured foil stacks
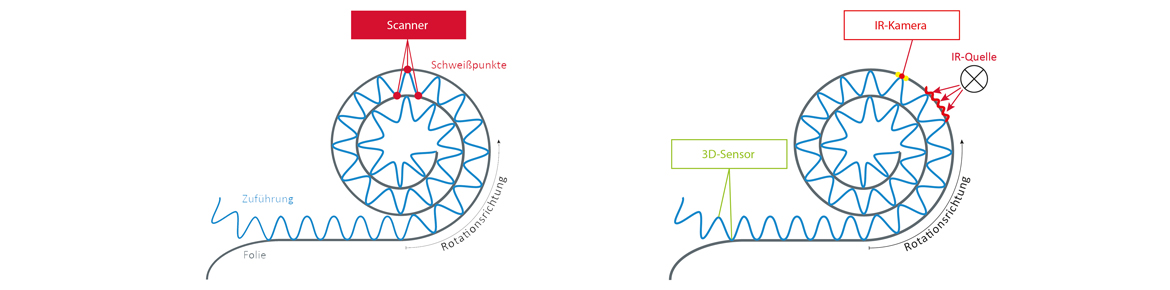
In order to be able to meet climate change, as a major social challenge, the recovery of energy is an efficient approach. Rotary heat exchangers, in which structured and unstructured foils are wound around a cylinder, are already being used for this purpose. They achieve efficiencies of up to 90 %. The disadvantage is that they are glued, which increases resource consumption. The adhesive bonds lead to more costly disposal and to reduced thermal conductivity in contrast to material-bonded joints. In the project, therefore, ifw Jena and TU Ilmenau will jointly develop a joining process to produce rotary heat exchangers, cooling lystems or catalytic converters with adhesive bonds by laser beam welding. The aim is to achieve a metal-to-material bond between the foils by means of an energy input that varies rapidly in terms of location and time, without having to use additional filler materials. The welds are made selectively on both the wave crest and wave trough of the structured film.
In parallel, the KorrMisch project (49 LBR) is investigating ways of making weld seams on metallic foils more corrosion-resistant. The findings from this project will be incorporated into the investigations in the PUNKT project.
In parallel, the KorrMisch project (49 LBR) is investigating ways of making weld seams on metallic foils more corrosion-resistant. The findings from this project will be incorporated into the investigations in the PUNKT project.
Project partner: Technische Universität Ilmenau, Fakultät Maschinienbau, Fachgebiet Qualitätssicherung und industrielle Bildverarbeitung